Focal Lobular Carcinoma In Situ: Insights and Implications

Intro
Focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) has emerged as a significant topic in breast pathology. As a non-invasive breast lesion, it presents a unique set of challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the nuances of FLCIS is crucial for both healthcare professionals and researchers. This article offers a comprehensive examination of FLCIS, its pathology, and the various clinical implications associated with this condition.
With the increased emphasis on individualized care plans, dissecting the characteristics of FLCIS can aid in improving patient outcomes. There is not only a need for clarity in identification and classification but also a growing demand for advanced management strategies tailored to unique patient profiles. This discussion aims to fill those gaps, guiding clinical practices and future research efforts.
Methodology
Study Design
This review of FLCIS utilizes an integrative approach by synthesizing existing literature and research studies. Various case studies, cohort studies, and clinical trials have been analyzed to provide a well-rounded view of the pathology.
Data Collection Techniques
Data is drawn from peer-reviewed journals, case reports, and comprehensive cancer databases focusing on breast oncology. Information regarding risk factors, diagnostic techniques, and treatment options has been compiled to achieve an accurate representation of FLCIS. Key terms such as "Focal Lobular Carcinoma In Situ," "non-invasive breast lesion," and "diagnostic challenges" provide a foundation for thorough research.
This systematic examination also looks into recent advancements in diagnostic imaging, such as mammography and ultrasound, as well as histological assessments that are crucial for detection and classification.
Discussion
Interpretation of Results
The analysis of gathered data indicates that early detection of FLCIS significantly influences treatment outcomes. The unique histopathological characteristics of FLCIS complicate differentiation from other neoplastic lesions, necessitating skilled interpretation. Despite being classified as a non-invasive entity, its potential risk for progression to invasive disease remains a focal point in management discussion.
Limitations of the Study
One limitation of this review is the variability in diagnostic criteria among different studies. The interpretation of FLCIS can vary significantly, leading to inconsistencies in reporting and subsequent treatment decisions. Additionally, the sample sizes in some studies may not represent the broader population effectively.
Future Research Directions
Further investigation is warranted in several areas:
- The genetic and molecular underpinnings of FLCIS.
- The long-term outcomes of patients diagnosed with FLCIS.
- Development of standardized diagnostic protocols.
Identifying the optimal clinical pathways and improving risk stratification methods may enhance how healthcare professionals manage FLCIS in diverse patient populations.
Prelude to Focal Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
Focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) is a significant pathology that presents unique features in the realm of breast oncology. Understanding FLCIS is crucial for medical professionals, as it influences both diagnostic and treatment strategies. Unlike invasive carcinomas, FLCIS is classified as a non-invasive lesion. This distinction has profound implications for patient management and therapeutic decisions.
Definition and Characteristics of FLCIS
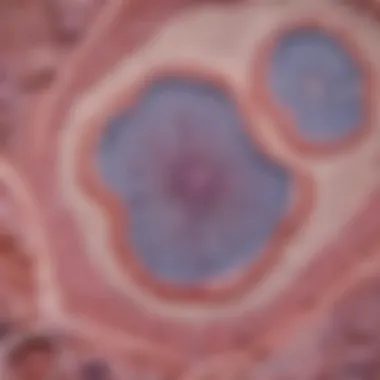
FLCIS is defined as an abnormal growth of cells in the lobules of the breast, which do not infiltrate surrounding tissues. This lesion is characterized by a lack of invasive components, differentiating it from invasive lobular carcinoma. The cells in FLCIS display alterations that can indicate potential future malignancy, necessitating careful observation and management. Key characteristics of FLCIS include:
- Non-invasive nature, which can make diagnosis challenging.
- Often identified during biopsies or imaging studies conducted for other reasons.
- Associated with a higher risk of developing invasive breast cancer over time.
Understanding these characteristics is vital for accurately diagnosing and managing patients with FLCIS.
Historical Context of the Diagnosis
The diagnosis of FLCIS has evolved over time. Initially, it was not recognized as a distinct entity within breast pathology, often overshadowed by more aggressive forms of breast cancer. The terminology and classification have undergone significant changes since the early days of breast pathology studies.
In the 1980s, FLCIS was first emphasized in the literature, allowing for better understanding among healthcare providers. Ongoing research has led to a clearer recognition of the biological behavior associated with this condition. It has reshaped clinical approaches, promoting specialized screening and monitoring strategies for affected patients. This historical context highlights the importance of continuous education in pathology, ensuring healthcare professionals remain updated on evolving definitions and implications of diagnoses like FLCIS.
"The management of focal lobular carcinoma in situ requires not only thorough knowledge but also a careful consideration of the implications for each patient."
This emphasis on historical development underscores the weight of evidence-based practices in guiding contemporary diagnostics and fostering appropriate patient care.
Pathophysiology of Focal Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
The pathophysiology of focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) represents a critical element in understanding this unique breast pathology. Recognizing the cellular changes and molecular behaviors associated with FLCIS provides insight into its non-invasive nature and potential implications for breast cancer progression. This section delves into the varied mechanisms at play, elucidating the cancer's characteristics and distinct differences from other carcinomas.
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms
FLCIS originates primarily from the lobular units of the breast, where abnormalities in cellular growth occur. At the molecular level, alterations in typical cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and adhesion properties can trigger the development of FLCIS.
Key mechanisms include the following:

- E-cadherin loss: One of the hallmark characteristics of lobular carcinoma is the loss of E-cadherin, a glycoprotein responsible for cell-cell adhesion. This loss leads to a more invasive phenotype, allowing cells to grow independently and acquire further mutations.
- Genetic mutations: Mutations in genes, such as CD and TP53, are frequently implicated in lobular breast cancers. These mutations can disrupt normal cellular function and may facilitate a microenvironment conducive to cancer development.
- Immune modulation: The immune response often plays a dual role in cancer biology. In FLCIS, changes in local immune cell populations can alter the tumor microenvironment. This can either promote tumorigenesis or help in restraining cellular progression.
Understanding these molecular mechanisms is vital for the formulation of targeted therapeutic strategies in the future, and they provide a foundational link in the ongoing research surrounding FLCIS.
Differences from Other Carcinomas
Focal lobular carcinoma in situ exhibits notable distinctions when compared to other types of breast carcinomas, such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). This differentiation is crucial for correct diagnosis and treatment selection.
Some key differences include:
- Cellular morphology: FLCIS cells often present in a more dispersed fashion, compared to the more cohesive structure observed in DCIS. This dispersion can complicate detection during imaging.
- Biological behavior: FLCIS is classified as a non-invasive lesion, with established evidence linking it to the development of invasive lobular carcinoma over time. In contrast, DCIS carries a higher risk of progression to invasive ductal carcinoma.
- Immunohistochemical profiles: Distinct biomarkers may be used to differentiate FLCIS from other types, which can include varied patterns of hormone receptor positivity or gene expression signatures that provide insight into their pathological behavior.
"Understanding the differences between FLCIS and other carcinomas is essential for appropriate management and accurate prognostic assessments."
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Understanding the epidemiology and risk factors associated with focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) is crucial for both researchers and clinicians. This knowledge can help in forming targeted screening and prevention strategies. It also offers insight into how these factors influence the diagnosis and management of the disease. Consequently, grasping the incidence rates and the underlying genetic and environmental risk factors provides a framework for better patient treatment plans.
Incidence Rates of FLCIS
FLCIS is considered a less common form of breast cancer compared to other invasive and non-invasive lesions. Recent studies indicate that the incidence rates are increasing, particularly in women over the age of 40. According to data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program, the annual incidence of FLCIS was approximately 1 in 100,000 women in the early 2000s. However, it has been observed that incidence rates have risen over the past decade, possibly due to increased screening practices and better awareness among healthcare providers.
Factors contributing to the increasing detection rates likely include:
- Improved imaging technologies such as mammography and MRI.
- Enhanced education on breast health, leading to earlier screening.
- Changes in reproductive patterns and lifestyle factors among women.
Genetic Predisposition and Environmental Factors
The interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental influences is complex and significant in the context of FLCIS. Certain genetic mutations can elevate the risk of developing FLCIS. For instance, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are known to increase breast cancer risk, including instances of FLCIS. Recent research suggests that the presence of these mutations may be linked with a higher likelihood of non-invasive cancers, thereby establishing a clear relation between genetics and risk.
In addition to genetic factors, environmental exposures also play a critical role:
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal replacement therapy during menopause has been associated with an increased risk of breast lesions like FLCIS.
- Lifestyle Choices: Factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and alcohol intake can contribute to a higher incidence of this pathology.
- Radiation Exposure: Prior radiation treatments for conditions such as Hodgkin's lymphoma can also elevate the risk of developing breast lesions, including FLCIS.
In summary, understanding the epidemiology and risk factors of FLCIS not only assists in early detection but also in tailoring prevention and management strategies. With continued research, more definitive correlations between genetic makeup, environmental exposures, and the etiology of FLCIS may emerge, guiding future clinical practices.
Diagnostic Techniques for FLCIS
Understanding the diagnostic techniques for Focal Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (FLCIS) is vital, as accurate diagnosis significantly influences management strategies and patient outcomes. FLCIS is often detected incidentally during routine breast screening. Identifying it swiftly and reliably can prevent the complications associated with misdiagnosis. Multiple imaging modalities and biopsy techniques play crucial roles in establishing a diagnosis and planning treatment. Here, we will delve deeper into these techniques, focusing on their unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations.
Imaging Modalities
Imaging techniques are fundamental tools in the diagnosis of FLCIS. They provide visual insights into breast tissue abnormality. The primary imaging modalities include mammography, ultrasound, and MRI, each with its own strengths.
Mammography
Mammography remains a first-line imaging modality for breast lesions. It harnesses low-energy X-rays to produce detailed images of the breast. The ability of mammography to detect microcalcifications makes it particularly valuable for identifying early-stage lesions like FLCIS.
A key characteristic of mammography is its ability to evaluate both breasts simultaneously, which enhances diagnostic accuracy. This makes it a beneficial choice in screening programs, aiming to detect breast cancer early. However, this method has limitations. Dense breast tissue can obscure lesions, resulting in false negatives. Patients with denser breasts may require supplemental imaging to ensure a complete evaluation.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound, utilizing sound waves, is a non-invasive imaging technique frequently used alongside mammography. It is particularly useful in evaluating palpable masses or specific areas of concern identified by mammograms.
One key characteristic of ultrasound is its real-time imaging capability, allowing for dynamic assessment of the lesion. This method is beneficial for differentiating between solid and cystic masses. However, one major disadvantage is its operator dependency; the accuracy can vary based on the expertise of the technician performing the ultrasound. Additionally, ultrasound may not be as effective for detecting small calcifications that often suggest FLCIS.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is increasingly being recognized for its role in breast cancer diagnosis, especially for high-risk patients. MRI employs strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images, providing excellent soft-tissue contrast.
The unique feature of MRI is its ability to assess the extent of disease more comprehensively than other modalities. It can visualize invasive components of cancer when present. Nonetheless, the cost and availability of MRI can limit its accessibility. Moreover, not every patient requires this level of investigation. Since MRI might produce false positives, it should complement other diagnostic techniques rather than replace them.
Biopsy and Histopathological Examination
After imaging, a biopsy is paramount for confirming the diagnosis of FLCIS. This involves extracting tissue samples for microscopic examination. Histopathological examination provides the definitive diagnosis and helps in assessing the nature of the lesion. Various biopsy techniques, including fine-needle aspiration or core needle biopsy, are utilized based on clinical context. They allow for targeted sampling of suspicious areas and have improved diagnostic accuracy.
In summary, the diagnostic landscape for FLCIS involves a careful selection of imaging modalities followed by histopathological analysis. Each method presents its own set of advantages and considerations, making the multidisciplinary approach essential for optimal patient management. Regular training and updates in methodologies can further enhance the effectiveness of these diagnostic techniques.
Clinical Management of FLCIS

The management of Focal Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (FLCIS) is crucial due to its unique characteristics and implications for patient care. It requires a comprehensive approach that considers both clinical and patient-specific factors. Understanding these elements can guide healthcare professionals in making informed decisions that affect long-term patient outcomes. FLCIS often presents ambiguities which necessitate individualized treatment plans. This section explores surgical options, radiation therapy considerations, and the balance between intervention and observation strategies.
Surgical Options
Surgery can be an effective management strategy for FLCIS, but it is not universally required. The main surgical method is lumpectomy, which involves the removal of the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue. This approach aims to reduce the risk of recurrence while preserving breast appearance.
- Lumpectomy: Effective for localized disease, it allows for further examination of the excised tissue. The presence of invasive components may alter the surgical plan.
- Mastectomy: In some cases, where there is a significant risk of progression to invasive cancer, a mastectomy may be suggested. This option is more radical and is often discussed after consultations with patients about risks and benefits.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Sometimes performed in conjunction with lumpectomy if invasive disease is suspected, emphasizing the need for careful assessment before surgery.
The decision regarding surgical interventions often involves multidisciplinary discussions, encompassing oncologists, surgeons, and radiologists. Each team member contributes their expertise, ensuring that the patient receives a comprehensive evaluation.
Radiation Therapy Considerations
Radiation therapy plays a vital role in the clinical management of FLCIS, particularly following surgical procedures like lumpectomy. Its primary purpose is to minimize the risk of recurrence in the breast.
- Adjuvant Radiation: Administered after breast-conserving surgery, it can significantly reduce the likelihood of local recurrence, especially in patients with margins that are close or positive.
- Techniques and Dosing: Various techniques exist, including whole breast radiation and partial breast radiation. The specific choice depends on individual cases, tumor characteristics, and surgical outcomes.
- Side Effects and Patient Well-Being: It is essential to discuss potential side effects, which can include fatigue and skin irritation. Patients should be informed to ensure they can make educated decisions about their treatment pathways.
Observation vs. Intervention Strategies
The management of FLCIS often presents a dilemma between observation and intervention. This decision greatly depends on the patient’s risk profile and preferences.
- Active Surveillance: In selected patients, particularly those at low risk or with limited lesions, active surveillance may be appropriate. This approach involves regular monitoring through imaging and clinical exams without immediate intervention.
- Immediate Intervention: For individuals with higher-risk features or those who express significant anxiety about progression, immediate intervention may be preferred. This could involve surgical options or radiation therapy.
- Patient Education: Vital in this decision-making process, educating patients about their condition, management options, and potential outcomes can lead to more tailored and satisfying care experiences.
The intersection of clinical judgment and patient input is essential, promoting personalized treatment that aligns with patient values and healthcare goals.
In summary, effective clinical management of FLCIS involves a multi-faceted approach, combining surgery, radiation therapy, and careful consideration of observation strategies. Each patient necessitates an individualized plan, reflecting the complexity of their diagnosis and circumstances.
Prognosis and Follow-Up Care
The prognosis and follow-up care for patients with focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) is an integral part of managing this non-invasive breast lesion. Proper understanding of long-term outcomes and the need for regular screening can significantly affect patient management strategies. Here, we delve into the specifics of prognosis, focusing on anticipated outcomes and the importance of follow-up protocols.
Long-Term Outcomes for Patients with FLCIS
Long-term outcomes for individuals diagnosed with FLCIS present a mixed picture. Research indicates that while FLCIS is classified as a non-invasive lesion, it does carry a risk of developing into invasive breast cancer over time. Studies suggest that about 20-30% of women with FLCIS may experience a progression to invasive disease within a decade of diagnosis.
This statistic calls for meticulous surveillance and a tailored follow-up plan for each patient. Factors such as age at diagnosis, family history, and individual risk profiles should inform the approach to postoperative management. Understanding these long-term risks allows healthcare providers to develop appropriate strategies addressing patient concerns regarding their overall prognosis.
Moreover, studies underscore that most patients with FLCIS who remain vigilant with regular check-ups and screenings tend to have favorable outcomes. These insights pivot on the premise that, despite its potential for progression, the term "in situ" reflects a critical turning point where early detection remains paramount.
Importance of Regular Screening
Regular screening is vital for patients diagnosed with FLCIS. The primary goal is to monitor for any signs of progression to invasive carcinoma. Patients should be educated on the necessity of adhering to their screening schedules.
Key reasons for prioritizing regular screenings include:
- Early Detection: Identifying any changes early can lead to more effective treatment options.
- Patient Empowerment: Being informed encourages active participation in one's care decisions.
- Risk Assessment: Consistent monitoring aids in reevaluating risk levels, adapting management plans accordingly.
Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare providers regarding symptoms, concerns, or changes they observe. This dialogue enhances the overall care experience and fosters a collaborative environment for navigating FLCIS management.
Ultimately, the focus on prognosis and follow-up care for FLCIS embodies the essence of proactive healthcare. It emphasizes the need for personalized strategies, combining clinical expertise with patient involvement to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Recent Advances in FLCIS Research
Research into Focal Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (FLCIS) is crucial for understanding the nuances of this non-invasive breast lesion. The advances in this area have the potential to reshape diagnostic and treatment strategies. There is a pressing need for in-depth exploration of FLCIS, specifically its biological behavior and long-term implications.
Recent studies have illuminated pathways involving cellular mechanisms that contribute to the development of FLCIS. This offers the chance for more precise risk assessment and management frameworks that can ensure better outcomes for patients. Moreover, understanding recent research findings can empower healthcare providers with necessary knowledge to address this unique pathology more effectively.
Current Studies and Trials
Ongoing clinical trials are essential in the context of FLCIS, as they probe multiple aspects of the disease. Some pivotal studies include assessments of the risk correlation between FLCIS and invasive breast cancer. These studies aim to establish if FLCIS is merely a marker of increased cancer risk or a precursor lesion that necessitates intervention.
Recent trials have focused on:
- Evaluating surveillance strategies to monitor patients post-diagnosis of FLCIS.
- Investigating whether specific demographic factors or genetic mutations correlate with disease progression.
- Understanding the histopathological characteristics that might predict the course of FLCIS in patients.
Additionally, efforts are underway to conceptualize better diagnostic imaging modalities that can enhance the precision of FLCIS detection.
Emerging Therapeutic Options
As new research surfaces, innovative therapeutic options are being explored for FLCIS. Many studies examine the efficacy of targeted therapies combined with conventional approaches. These options could mitigate the risk of progression to invasive disease.


Some of the emerging therapeutic strategies include:
- Hormonal therapies: Particularly for patients with hormone receptor-positive FLCIS, agents like tamoxifen may offer preventive benefits.
- Molecular targeted therapies: Investigational trials into agents that inhibit specific molecular targets related to breast cancer growth and dissemination.
- Vaccination strategies: Immunotherapy approaches that focus on stimulating the body's immune system to fight off pre-cancerous lesions are being evaluated.
"Emerging treatments may make it possible to turn the tide against FLCIS, providing patients with more options and better overall outcomes."
The evolution of therapeutic strategies surrounding FLCIS offer a glimpse into a future where personalized medicine is more prominent, and where treatment plans can be tailored based on individual risk profiles. Understanding the implications of these advancements is fundamental for both clinicians and patients.
Implications for Clinical Practice
Understanding the implications of focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) is crucial for enhancing clinical outcomes. Practitioners must be well-versed in the unique characteristics of this condition to optimize patient management and treatment strategies. This section will explore the benefits of a multidisciplinary approach to care, emphasizing the need for collaboration among various health professionals to address the complex nature of FLCIS. Moreover, patient education and informed consent play a pivotal role in empowering individuals diagnosed with this condition, leading to more informed health choices.
Multidisciplinary Approaches to Care
Adopting a multidisciplinary approach is essential in managing patients with FLCIS. This method involves the integration of specialists from various fields, including oncologists, radiologists, pathologists, and surgical teams. Each specialist contributes their expertise, thus forming a comprehensive care plan tailored to the unique needs of the patient.
- Collaboration Enhancements: A cohesive treatment plan can be developed through discussions among specialists. For example, oncologists can inform surgical decisions about the best techniques, while pathologists can provide insights into the tumor's characteristics.
- Holistic Care: This approach ensures that all aspects of a patient’s care are considered. Physical, emotional, and social factors are integrated, providing a well-rounded strategy for treatment.
- Improvements in Outcomes: Studies indicate that multidisciplinary teams can lead to improved patient satisfaction and better clinical outcomes. Patients receiving coordinated care often report a greater understanding of their condition and treatment choices.
Involving multiple disciplines allows healthcare providers to ensure that patients receive not only the best possible medical treatment, but also psychological support through counseling and educational resources. This comprehensive consideration is vital in improving overall patient well-being and prognosis.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Patient education is vital in fostering a collaborative doctor-patient relationship in cases of FLCIS. Understanding the diagnosis, treatment options, and potential outcomes empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health.
- Information Accessibility: Educational materials should be tailored to be clear and accessible. This can include pamphlets, workshops, or online resources that explain FLCIS in layman's terms.
- Informed Decision-Making: Informed consent is more than just a bureaucratic step; it signifies that the patient comprehensively understands their condition. It involves discussions about risks, benefits, and alternatives of various treatment options.
- Coping Strategies: Providing information on potential psychological impacts, including anxiety or uncertainty surrounding a diagnosis, is essential. Understanding these factors can lead patients to seek necessary emotional support from healthcare teams.
"Engaged patients often show greater satisfaction and improved adherence to treatment plans."
Patient education also requires the continuous evolution of communication strategies. Healthcare providers must remain current with research and guidelines regarding FLCIS, ensuring that patients receive up-to-date and accurate information. An informed patient is better positioned to navigate their health journey, fostering a sense of control and involvement in their care.
Psychosocial Aspects of FLCIS Diagnosis
Focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) presents not only medical challenges but also significant psychosocial implications for patients. Understanding these aspects is crucial for holistic patient care. The diagnosis of FLCIS is often unexpected, creating profound emotional turmoil. Patients may experience anxiety, fear, or confusion about their health and future. Therefore, it is essential to acknowledge these feelings and address the psychological needs associated with this diagnosis.
FLCIS is frequently perceived as a precursor to invasive carcinoma, which can lead to distressing thoughts about potential treatment and the risk of recurrence. This uncertainty can impact a patient’s quality of life, making it necessary for healthcare providers to integrate support systems and information throughout the management process.
Impact on Quality of Life
The impact of FLCIS on a patient's quality of life can be significant. Being diagnosed often leads to emotional and psychological distress. Patients may feel isolated, as they might not know anyone else who has faced similar experiences.
- Emotional Reactions: Feelings like depression and anxiety are common. Patients may feel a loss of control over their health. This emotional burden can affect day-to-day living and relationships.
- Fear of the Future: Concerns about cancer development and the implications of treatment choices can overwhelm individuals. This fear might lead to avoidance behaviors, potentially delaying important medical appointments or preventive measures.
- Social Withdrawal: Some patients may withdraw from social interactions, further exacerbating feelings of loneliness.
Recognizing and addressing these emotional difficulties is critical for health professionals. Supportive counseling and patient education can play a pivotal role in improving quality of life.
Support Systems and Resources
Access to support systems and resources is vital for those navigating the challenges of FLCIS. These resources can empower patients, offering guidance and companionship throughout their journey.
- Counseling Services: Professional counseling can help patients cope with the emotional aspects of diagnosis. Therapists can provide strategies to manage anxiety and depression.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand similar struggles can relieve feelings of isolation. Support groups, whether in-person or online, provide a space for sharing experiences and exchange valuable information.
- Educational Resources: Information about FLCIS, its implications, and management options can help reduce uncertainty. Local healthcare facilities and trusted online platforms like Wikipedia offer valuable content.
- Family and Friends: Encouraging the involvement of family and friends creates a strong support network. Educating loved ones about the condition can enable them to provide appropriate support.
Overall, understanding the psychosocial aspects of FLCIS diagnosis is essential. Addressing emotional and psychological needs can enhance patients' quality of life. Offering proper resources and support systems will contribute to a more comprehensive care approach.
"The emotional impact of a cancer diagnosis can often be as critical as the physical implications, underscoring the importance of addressing both."
By recognizing these factors, healthcare professionals can contribute positively to the patient's journey.
Future Directions in FLCIS Studies
The landscape of research surrounding focal lobular carcinoma in situ (FLCIS) is continually evolving, driven by the desire for deeper understanding and improved patient outcomes. This section emphasizes the critical need for ongoing investigation into FLCIS, focusing on specific areas that require attention. Studying these directions not only enhances the understanding of the disease but also informs clinical practice, ensuring healthcare professionals are equipped with the latest knowledge.
Given its complex nature, there are several potential areas for exploration that researchers should consider.
Potential Areas for Exploration
Several fronts exist for future exploration to augment current understanding of FLCIS:
- Genetic Profiling: Exploring the genetic mutations associated with FLCIS could reveal insights into its pathogenesis and help identify patients at higher risk.
- Longitudinal Studies: Conducting studies that follow patients over long periods can provide data on the natural history of FLCIS, further informing treatment protocols.
- Treatment Outcomes: Researching the efficacy of various treatment modalities and comparing patient outcomes can guide future therapeutic directions and strategies.
- Interactions with Hormones: Investigating the relationship between hormonal treatments and FLCIS could illuminate possible preventive strategies for at-risk populations.
These areas underscore the importance of research initiatives that can produce significant findings, guiding healthcare professionals and enhancing patient care.
Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies
The advancement of diagnostic technologies represents another critical front in FLCIS studies. Improved methods can lead to earlier detection and better stratification of risk, ultimately influencing treatment plans:
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: Innovations in mammography and MRI technology, including 3D imaging, allow for more precise detection and characterization of FLCIS.
- Biomarker Development: Identifying specific biomarkers related to FLCIS can assist in diagnosing and monitoring disease progression.
- Artificial Intelligence: Utilizing AI in imaging analysis is promising to improve detection rates and reduce false positives.







