Anaplastic Carcinoma of the Thyroid: A Comprehensive Overview


Intro
Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid is recognized as one of the most aggressive forms of thyroid malignancies. This rare cancer, while making up only a small percentage of thyroid cancers, is notably invasive and presents significant challenges in both diagnosis and treatment. Its pathophysiology indicates rapid cell multiplication, leading to swift tumor growth that complicates effective management approaches.
The rarity of anaplastic carcinoma can lead to delays in diagnosis, as symptoms often mimic those of less aggressive thyroid diseases. These factors underscore the importance of exploring its characteristics thoroughly. A comprehensive understanding of the disease aids clinicians in making timely decisions that could impact patient outcomes significantly.
This article intends to delve into various fundamental aspects of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, including its clinical presentation, diagnostic challenges, therapeutic options, and the implications for patient care. Furthermore, we will discuss recent advancements in research that promise to shed light on future management strategies and enhance outcomes for affected individuals.
Methodology
Study Design
This article synthesizes recent literature and clinical studies addressing anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. By employing a systematic review approach, pertinent studies have been identified and analyzed to construct a well-rounded narrative surrounding the disease. The objective is to provide clear insights into how this type of cancer affects patients and the current state of treatment methodologies.
Data Collection Techniques
Data collection involved reviewing peer-reviewed articles, clinical practice guidelines, and relevant case studies. Sources such as PubMed and the National Cancer Institute were utilized for compiling a comprehensive database of findings. This iterative process ensured that only the most relevant information informs our discussion on anaplastic carcinoma.
Discussion
Interpretation of Results
The findings suggest that early detection remains paramount in treating anaplastic carcinoma. Presenting symptoms can include neck swelling, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing, often arising as the disease progresses. Patients diagnosed at an early stage have better survival rates compared to those diagnosed late, highlighting the need for heightened awareness within both the medical community and the public about the signs of thyroid disorders.
Limitations of the Study
One limitation of this review is the varying methods of treatment and diagnostic criteria across different studies. These discrepancies can impact the comparability of results. Additionally, given the rarity of the disease, the available data is often limited to small sample sizes, which can hinder the robustness of conclusions drawn.
Future Research Directions
Future research should focus on large-scale studies to establish standardized treatment protocols. Additionally, exploring the genetic and molecular characteristics of anaplastic carcinoma could open avenues for targeted therapies. There exists a critical need for ongoing scientific inquiry to enhance understanding and improve patient outcomes in this aggressive cancer type.
This type of cancer, while rare, demands immediate attention and understanding due to its aggressive nature and poor prognosis.
Preface to Anaplastic Carcinoma of the Thyroid
Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid is a subject of great significance in oncological study due to its aggressive nature and associated challenges. Understanding this malignancy is critical not just for medical professionals, but also for researchers and educators focused on cancer biology. This cancer variant, while rare, demands a nuanced comprehension of its characteristics, because it starkly contrasts with more common forms of thyroid cancer.
This section serves to provide a foundational overview that underscores the urgency for research and awareness surrounding anaplastic carcinoma. It is essential to recognize that early diagnosis can lead to more effective management and potentially improve patient outcomes. Moreover, the multifaceted nature of this disease necessitates an examination of its definition, classification, and the latest epidemiological data to inform clinical practice and research agendas.
Definition and Classification
Anaplastic carcinoma is typically defined as a poorly differentiated thyroid cancer that exhibits aggressive behavior. It arises from follicular cells of the thyroid, which are responsible for producing thyroid hormones. Unlike differentiated thyroid cancers, such as papillary or follicular carcinoma, anaplastic carcinoma grows rapidly, making it a medical emergency.
In terms of classification, anaplastic carcinoma can be categorized based on histological features into three main types:
- Giant cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Undifferentiated carcinoma
Each subtype has distinct biological behaviors and implications for treatment strategies. Recognizing these differences is crucial for developing an effective therapeutic approach, as they influence prognosis and management decisions.
Epidemiology
The epidemiology of anaplastic carcinoma reveals a rare occurrence among thyroid malignancies, constituting about 1% to 2% of all thyroid cancer cases. Its incidence appears to be increasing, which highlights the need for ongoing research in this area.
Key epidemiological points include:
- This cancer usually manifests in individuals over the age of 65, with a median survival time post-diagnosis nearing five months.
- Gender disparities exist, as it is more prevalent in women than men, although the reasons for this difference are not thoroughly understood.
- Environmental and genetic factors may also play a role, suggesting that further studies are required to determine risk factors.
Pathophysiology of Anaplastic Carcinoma
Understanding the pathophysiology of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid is crucial for grasping how the disease develops and progresses. Anaplastic carcinoma is known for its aggressive nature and rapid deterioration of health. Recognizing the biological underpinnings can aid in refining diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. This section delves into the genetic mutations involved and the tumor microenvironment that facilitates the malignancy's growth.
Genetic Mutations and Alterations
Anaplastic carcinoma often arises from pre-existing well-differentiated thyroid cancers, such as papillary or follicular thyroid carcinoma. These tumors undergo genetic alterations leading to their transformation into the anaplastic form. Key mutations include changes in the TP53 gene; mutations in BRAF and PIK3CA are also noted. These genetic variations contribute to a loss of differentiation, increased proliferative capacity, and resistance to apoptosis.
Specific genetic changes result in aggressive tumor behavior. The TP53 mutations are particularly significant as they disrupt normal cell cycle regulation. Furthermore, BRAF mutations are prevalent in various thyroid cancers, influencing signaling pathways that promote tumor survival and proliferation.
The mutations lead to the activation of oncogenic pathways and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes. This combination results in uncontrolled cellular growth and the potential for metastasis. Furthermore, anaplastic carcinoma has a high degree of genomic instability which complicates treatment and reinforces its malignancy.
In summary, genetic alterations are central to the transformation of thyroid cells into anaplastic carcinoma, significantly impacting the course of the disease.
Tumor Microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment in anaplastic carcinoma plays a vital role in supporting tumor growth and progression. It consists of extracellular matrix components, immune cells, blood vessels, and signaling molecules that together create a conducive niche for cancer cells.
The microenvironment can influence tumor behavior, aid in evading immune response, and enhance metastatic potential.
Anaplastic carcinoma often demonstrates an interplay between tumor cells and stromal elements. The surrounding stroma can provide growth factors that support tumor survival. For instance, a presence of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) can promote invasion and metastasis through secretion of cytokines.
Additionally, the vascularization of the tumor allows for increased nutrient supply, further aiding in rapid growth. The presence of certain immune cells is paradoxical; while they may attempt to mount an immune response, they can also inadvertently support tumor growth through immune suppression mechanisms.
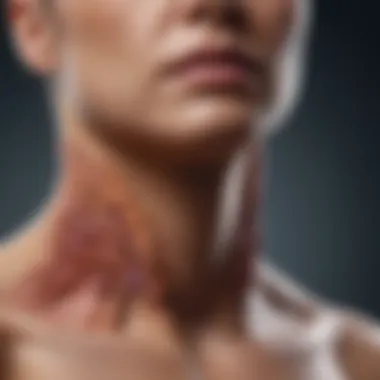

Clinical Presentation
Understanding the clinical presentation of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid is crucial for both diagnosis and management. This section delves into the symptoms and signs that are essential in identifying this aggressive cancer form. A clear grasp of these clinical insights aids healthcare practitioners in making informed decisions, leading to better patient outcomes.
Symptoms and Signs
Anaplastic carcinoma is known for its rapid progression. The most common symptoms include a rapidly enlarging neck mass. In many cases, patients may present with hoarseness or changes in voice due to invasion of the surrounding structures. Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is also prevalent. Other symptoms may encompass:
- Thyroid Pain: Patients often report local discomfort or pain in the neck region.
- Respiratory Distress: Advanced cases may obstruct the airway, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can occur due to cancer’s metabolic impact.
- Fatigue: Many patients exhibit significant fatigue, a common symptom in malignancies.
These symptoms typically emerge quite suddenly, often misleading patients by appearing benign initially. The aggressive nature of the disease makes recognizing these signs even more important.
Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing anaplastic carcinoma poses significant challenges. This cancer type can mimic other entities, which may lead to misdiagnosis. Some key diagnostic hurdles include:
- Biopsy Limitations: A fine-needle aspiration biopsy may fail to capture the aggressive qualities of the tumor. Thus, obtaining a representative sample can be problematic.
- Histological Overlap: Anaplastic carcinoma can resemble other high-grade thyroid cancers. Distinguishing between them requires advanced expertise.
- Advanced Disease Stage: Many patients present at an advanced stage, complicating diagnosis and treatment options.
- Imaging Difficulties: Standard imaging techniques may not always determine the extent of the disease accurately, potentially delaying necessary interventions.
The urgency in addressing these challenges lies in the disease's dire prognosis. Misdiagnosis or late diagnosis can significantly impair treatment efficiency and survival chances.
Proper recognition of symptoms alongside overcoming diagnostic obstacles is essential for ensuring timely and effective care for patients afflicted with anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid.
Diagnosis of Anaplastic Carcinoma
The diagnosis of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid is a critical component in the management of this aggressive cancer. Early and accurate diagnosis can significantly impact treatment outcomes and overall patient survival rates. Due to the swift progression of the disease, reliance on advanced diagnostic techniques becomes imperative. This section will explore imaging techniques and histopathological assessments, integral to identifying and confirming the presence of anaplastic carcinoma.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a vital role in the diagnosis of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. These modalities help visualize the anatomical structure and the extent of the tumor. Common imaging tests include ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Ultrasound is often the first step in thyroid evaluation. It helps in assessing nodule characteristics such as size, morphology, and echogenicity. This technique is crucial for detecting suspicious nodules that may warrant further investigation.
- CT scans provide cross-sectional images that allow for a more comprehensive understanding of the tumor's relationship with surrounding structures. They can help identify local invasion, which is critical for staging and treatment planning.
- MRI may be utilized in particular cases where soft tissue detail is necessary. It is especially useful for assessing the involvement of neighboring tissues and for planning surgical interventions.
Ultimately, these imaging techniques not only aid in diagnosis but also inform the surgical and therapeutic approaches to managing the disease.
"Accurate imaging is essential in the stratification of patients with thyroid carcinoma, guiding treatment decisions effectively."
Histopathological Assessment
Histopathological assessment remains a cornerstone in diagnosing anaplastic carcinoma. This process involves examining tissue samples obtained through fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or surgical resection. The primary goal is to identify the unique cellular characteristics indicative of anaplastic thyroid cancer.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB): This minimally invasive procedure is often the first line for obtaining thyroid tissue samples. Cytological evaluation can reveal cellular atypia and other features suggestive of malignancy. However, FNAB may not always yield definitive results, particularly in cases where there is a mixture of cancer types.
- Histological Examination: Once tissue samples are obtained, pathologists use various staining techniques to evaluate the cells under a microscope. Anaplastic carcinoma exhibits distinctive features such as pleomorphic cells, high mitotic activity, and necrosis. These characteristics are vital for differentiation from other thyroid neoplasms.
- Immunohistochemistry: This technique further enhances the diagnostic accuracy by identifying specific tumor markers. Anaplastic carcinoma typically expresses markers such as p53 and can have variable expression of thyroglobulin, further aiding in diagnosis.
Treatment Modalities
In managing anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid, it is vital to explore diverse treatment modalities. This approach can enhance patient outcomes and address the aggressiveness of the disease. The treatment plan often involves multiple components, including surgical options, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and newer targeted therapies. Each modality carries its own benefits and considerations. Understanding these can guide clinical decisions and provide insights for ongoing research.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical intervention is often considered the first-line treatment for anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. The primary goal is often to achieve complete resection of the tumor when feasible. However, due to the aggressive nature of this cancer, surgery can be challenging.
Key points regarding surgical interventions include:
- Radical Surgery: Total thyroidectomy is frequently performed. However, in some cases, subtotal resection might also be considered depending on tumor size and local invasion.
- Resectability: Understanding the extent of the disease is crucial. In cases where tumors metastasize extensively, surgery may not be possible, leading to alternative treatment considerations.
- Complication Risks: Surgical risks, including voice changes and hypoparathyroidism, should be communicated to patients and their families. This informed consent is essential for setting realistic expectations.
Overall, effective surgical management hinges on a thorough assessment of the tumor characteristics and the patient's overall health.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy plays an important role in treating anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid, especially for patients where complete surgical resection is not achievable. It can serve as adjuvant therapy post-surgery or as a primary treatment for inoperable tumors.
Some critical aspects of radiation therapy include:
- Techniques: Options such as external beam radiation therapy and radioactive iodine can be utilized, depending on the specific clinical scenario.
- Relief of Symptoms: It often provides palliation for patients with symptoms from locoregional disease, such as pain and dysphagia.
- Outcomes: Studies suggest that radiation therapy can enhance overall survival rates and reduce local recurrence, adding another layer of treatment efficacy.
Patients should be made aware of side effects, which can include skin irritation and fatigue, to manage their expectations effectively.
Chemotherapy Approaches
Chemotherapy has a complex role in the management of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. Since this type of cancer is often resistant to traditional chemotherapy agents, its application is selective.
Considerations regarding chemotherapy include:
- Combination Regimens: Some recent studies explore the use of combination therapies. These may incorporate traditional chemotherapeutic agents like doxorubicin along with newer drugs.
- Cytotoxicity: The aggressiveness of anaplastic carcinoma often limits the effectiveness of chemotherapy. Careful evaluation of the potential benefits versus adverse events is crucial before initiation.
- Clinical Trials: Ongoing research into novel combinations is critical. Engaging patients in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatment options that may yield better outcomes.
Targeted Therapies
The advent of targeted therapies marks a significant advancement in the treatment of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. These therapies focus on specific molecular targets that drive tumor growth, making them potentially more effective than conventional therapies.
Key highlights include:
- Drug Examples: FDA-approved agents like lenvatinib and sorafenib target the VEGFR and RAF pathways, showing promise in clinical settings.
- Personalized Medicine: Understanding genetic alterations that characterize anaplastic carcinoma can guide the selection of targeted therapies, thereby personalizing treatment protocols to improve response rates.
- Future Directions: Research into additional molecular targets is ongoing, providing hope for developing more effective treatments that could reshape the management landscape of anaplastic carcinoma.


In summary, the treatment modalities for anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid are multifaceted, combining surgical, radiological, chemotherapeutic, and novel targeted approaches to address the unique challenges posed by this aggressive malignancy.
Prognosis and Outcomes
The prognosis for anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid is often poor due to its aggressive nature. Understanding the prognosis and outcomes of this malignancy is crucial for patients and clinicians alike. This section examines survival rates and the factors influencing prognosis. These elements help in assessing treatment efficacy and tailoring management strategies.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for anaplastic carcinoma are notably low. Research indicates that the overall 1-year survival rate is around 20% to 30%. The 5-year survival rates are even less favorable, commonly cited at under 10%. Factors such as the stage at diagnosis, the patient’s age, and overall health can influence these numbers significantly.
- Early Detection: Identifying anaplastic carcinoma in its early stage may provide a slight edge in survival.
- Treatment Response: Some individuals may respond better to treatment, potentially improving outcomes, albeit marginally.
These statistics highlight the challenge of managing such an aggressive form of cancer. Patients often face rapid disease progression, leading to limited treatment options and necessitating a focus on the quality of life.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors can dictate a patient’s prognosis with anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. These include:
- Age: Younger patients tend to have a better prognosis compared to older patients.
- Tumor Size: Larger tumors often correlate with worse outcomes.
- Histological Features: Specific features observed under histopathological examination can provide insight into the tumor's behavior.
- Comorbid Conditions: Patients with additional health concerns may experience poorer outcomes due to their reduced overall health status.
- Response to Initial Treatments: Early and aggressive treatment responses can sometimes lead to improved survival rates.
"Understanding the multifactorial nature of prognosis can aid clinicians in formulating effective treatment plans."
In summary, the prognosis of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid is grim, but specific factors can provide a clearer picture of the expected outcomes. Individual patient assessments are critical for optimizing management strategies.
Recent Advances in Research
Recent advances in research pertaining to anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid have ushered in new hope for patients and healthcare providers alike. These developments are pivotal for enhancing understanding and treatment of this aggressive disease. They also provide insights that could lead to more personalized therapies and improved patient outcomes. The growing comprehension of underlying mechanisms and pathways in anaplastic carcinoma opens avenues for novel interventions, which may ultimately mitigate its poor prognosis.
Novel Therapeutic Agents
The quest for novel therapeutic agents in the fight against anaplastic carcinoma is ongoing. Recent studies have identified various compounds that target specific pathways involved in tumor growth and metastasis. For example, lenvatinib is a multi-kinase inhibitor currently showing promise in clinical settings. It targets multiple kinase receptors, which are involved in tumor proliferation and angiogenesis.
Another example is dabrafenib, which targets BRAF mutations prevalent in some cases of anaplastic carcinoma. The application of these targeted therapies has demonstrated a potential to improve response rates and prolong survival, compared to traditional methods. Researchers continue to explore combinations of these agents with existing treatments, such as immunotherapies, to enhance their efficacy further.
Incorporating immunotherapy is particularly notable. Drugs such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab are allowing for a more personalized approach, taking advantage of the patient's own immune system to fight cancer. This transition from standard therapies to targeted agents reflects the larger trend in oncological research towards tailored treatment regimens.
Biomarkers in Anaplastic Carcinoma
Biomarkers play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing anaplastic carcinoma, guiding both treatment options and predicting patient outcomes. Recent research has identified several biomarkers that may aid in this regard. For instance, the presence of TP53, BRAF, and HRAS mutations are increasingly recognized as significant indicators of the disease's aggressiveness.
"Identifying specific genetic mutations helps clinicians tailor treatments to individual patients, improving outcomes."
The temporal monitoring of these biomarkers may also facilitate the early detection of recurrence after treatment. Blood-based assays that evaluate circulating tumor DNA are being developed to provide real-time insights into tumor dynamics. This real-time monitoring could revolutionize management strategies, allowing for rapid intervention when necessary.
Furthermore, the integration of biomarkers in clinical trials is enhancing our understanding of the disease and contributing to evidence-based guidelines. The careful evaluation of these markers in relation to patient responses is critical to advancing therapeutic approaches.
In summary, the recent advances in research not only illuminate the complexities of anaplastic carcinoma but also provide exciting pathways for new therapeutics and diagnostic strategies, tailored to the individual nuances of this challenging disease.
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
Case studies and clinical trials play a pivotal role in understanding anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. They provide real-world evidence that can lead to better treatment strategies and improved patient outcomes. Anaplastic carcinoma is known for its aggressive nature and a poor prognosis. Thus, investigating individual cases can reveal critical insights into its progression, clinical characteristics, and effectiveness of various treatment modalities.
Through case studies, healthcare professionals can document unusual presentations, treatment responses, or complications that arise in managing this disease. These reports often highlight how individualized approaches can influence patient outcomes. Understanding the unique challenges faced by patients helps in refining management protocols and addressing specific needs.
Moreover, clinical trials are essential in establishing evidence-based guidelines. They test new therapies and strategies aimed at improving survival rates and quality of life. In anaplastic carcinoma, where treatment options may be limited due to the rapid progression of the disease, the results from clinical trials can introduce novel therapeutics and reshape existing treatment frameworks.
Effective management of anaplastic carcinoma requires ongoing research to identify the most beneficial treatment options for patients.
Another important aspect is the ethical considerations associated with case studies and clinical trials. Researchers must navigate the complexities of informed consent, especially in populations where cognitive function may be impaired due to illness. Ensuring that the rights and welfare of patients are protected is paramount.
In summary, the integration of case studies and clinical trials into clinical practice not only enhances knowledge but also helps form the basis for future research directions. They are fundamental in illustrating the spectrum of anaplastic carcinoma, guiding prognostic assessments, and influencing treatment protocols.
Notable Case Reports
Notable case reports in anaplastic carcinoma serve as critical points of learning for clinicians. These reports often describe specific patient journeys, including their presenting symptoms, diagnostic challenges, treatment choices, and outcomes. For instance, a report might detail a patient who experienced rapid lymphatic spread despite initial responses to treatment. Such cases can illuminate how varying biological behaviors of tumors can lead to unexpected clinical outcomes.
Furthermore, notable cases often help in highlighting the diversity in presentations of anaplastic carcinoma. Reports may include incidents of lung metastasis at the time of diagnosis or those that illustrate the challenges with co-existing conditions, impacting treatment readiness and approaches.
Impact of Clinical Trials on Treatment Guidelines
The impact of clinical trials on treatment guidelines cannot be overstated. Clinical trials provide a rigorous framework for investigating the efficacy of new therapies against established benchmarks. They assess not just survival benefits but also side effects, quality of life, and cost-effectiveness of interventions in anaplastic carcinoma. Evidence derived from these trials informs clinicians on what approaches yield the best outcomes and helps in making data-driven decisions.
For instance, trials testing targeted therapies such as lenvatinib or sorafenib have transformed the pharmacological landscape of treatment options available, allowing practitioners to offer patients innovative options tailored to their specific tumor profiles.
In essence, clinical trials not only inform existing treatment frameworks but also catalyze the development of emerging treatment modalities, thus fostering continuous evolution in managing anaplastic carcinoma.
Challenges in Management
The management of anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid presents various challenges that are crucial in understanding the implications for patient treatment and outcomes. This aggressive form of cancer is not only complex but also demands a multi-faceted approach to address its unique characteristics. One of the primary concerns is the rapid progression of the disease, which complicates early diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
Resistance to Treatment
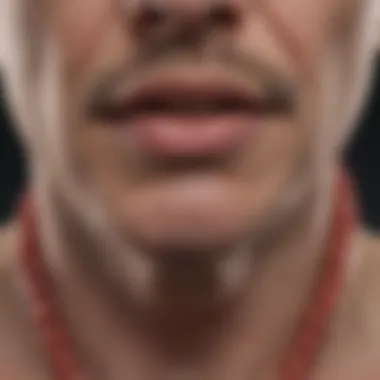

Resistance to treatment is a significant issue when dealing with anaplastic carcinoma. This type of cancer often does not respond to standard treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy and radiation. The tumor's inherent biological heterogeneity can lead to various genetic mutations that render common therapeutic protocols ineffective. As a result, oncologists face an uphill battle in tailoring effective treatment regimens for these patients.
Factors Contributing to Treatment Resistance
- Genetic Mutations: As previously discussed, the mutations in genes such as TP53 and BRAF can alter tumor behaviors, decreasing responsiveness.
- Tumor Microenvironment: The microenvironment facilitates tumor growth and protects it from systemic therapies. This includes immune evasion and enhanced survival mechanisms.
- Previous Treatments: Patients with prior thyroid cancers might also have tumors that become increasingly resistant due to pre-existing therapies.
The interplay of these factors highlights the need for continual research into innovative treatment strategies and molecular targeting.
Palliative Care Considerations
Palliative care plays an essential role in the management of patients with anaplastic carcinoma. Given the poor prognosis associated with this type of cancer, focusing on the quality of life is paramount. Palliative care aims to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being rather than solely focusing on curing the disease.
Importance of Palliative Care
- Symptom Management: Patients often face debilitating symptoms such as pain, dysphagia, and fatigue. Timely palliative care interventions can significantly improve comfort.
- Psychosocial Support: Addressing the emotional and psychological needs of patients and their families is crucial. Palliative care providers can help navigate the complexities of managing terminal illness.
- Multi-Disciplinary Approach: Effective palliative care should involve a team of healthcare professionals, including oncologists, nurses, and social workers. This collaborative effort can ensure comprehensive care tailored to individual patient needs.
"Palliative care is not about the end of life; it is about improving the quality of life for patients at any stage of disease."
The integration of palliative principles into the management of anaplastic carcinoma not only eases suffering but also empowers patients and families to make informed decisions regarding care avenues. By recognizing the significance of both resistance to treatment and palliative considerations, healthcare providers can better navigate the multifaceted landscape of this complex cancer.
Patient Perspectives and Considerations
Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid can drastically change a patient's experience of illness. Understanding the patient perspective is vital for effective treatment and care. These insights can guide healthcare providers in addressing not only the physical aspects of the disease but also the emotional and social burdens that accompany it.
Quality of Life Issues
Patients diagnosed with anaplastic carcinoma often face significant challenges regarding their quality of life. This cancer type is aggressive and usually leads to a rapid decline in health. The impact of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation on everyday functions must not be overlooked. Common issues include:
- Fatigue: Many patients report extreme tiredness, which can persist long after treatment.
- Pain: Pain management can be a crucial aspect of care, as many patients suffer from discomfort due to tumor pressure or post-operative complications.
- Swallowing Difficulties: As the disease progresses, patients may encounter challenges with eating and drinking, impacting nutrition and overall well-being.
Another critical element is the emotional toll of a diagnosis of anaplastic carcinoma. Feelings of anxiety, fear, and depression are prevalent among patients. These emotional responses can interfere with the recovery process and inhibit compliance with treatment regimens.
Psychosocial Impact
The psychosocial effects of anaplastic carcinoma extend beyond the individual patient to their families and social networks. Patients often experience a sense of isolation due to their illness, creating barriers that can prevent open communication with loved ones.
Key aspects include:
- Emotional Support Needs: Patients often require support from friends and family. Encouraging open dialogue can help alleviate feelings of isolation.
- Support Groups: Participation in groups designed for cancer patients can foster a sense of community and shared experience. Sharing struggles and victories can be empowering.
- Role Changes: Patients may experience shifts in their roles within their families, such as taking on more of a dependent position. This change can lead to tension and emotional distress.
"Support and understanding from family are critical for coping with the stress of cancer diagnosis and treatment."
Future Directions in Anaplastic Carcinoma Research
The field of anaplastic carcinoma research is evolving, underscoring a critical need for innovative strategies in understanding and managing this aggressive malignancy. As we delve into future efforts, the focus should be on enhancing early detection, improving treatment modalities, and ultimately offering better patient outcomes. The importance of this research cannot be overstated, as it holds the potential to transform the landscape of care for patients diagnosed with this rare form of thyroid cancer.
Emerging Trends in Treatment
In recent years, there have been notable advancements in treatment options for anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. Emerging therapies focus on targeted agents that can specifically combat the genetic mutations often present in this type of cancer. One such area is the exploration of combination treatments. This approach may enhance effectiveness and target possible resistance mechanisms.
Moreover, immunotherapy is taking center stage. Research indicates that certain patients may benefit from treatments that harness the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. This trend highlights the importance of ongoing clinical trials that evaluate the efficacy of such approaches.
Some key points in emerging trends include:
- Checkpoint inhibitors: These agents can potentially reactivate immune responses against tumors.
- Targeted therapy: New, personalized treatments can work against genetic profiles of tumors.
- Combination therapies: Using multiple treatments concurrently may yield synergistic effects.
Integrative Approach to Management
Integrative management of anaplastic carcinoma recognizes the need for a holistic view of treatment strategies that encompass not just medical therapies, but also lifestyle interventions and psychosocial support. This approach aims to improve the overall quality of life for patients.
Incorporating elements such as nutrition, physical activity, and psychological care creates a comprehensive treatment plan. Collaboration among healthcare professionals is essential to address the multidimensional needs of patients. When patients are engaged in their treatment, adherence improves, leading to better outcomes.
Some important aspects of integrative management include:
- Patient education: Informing patients about their condition and treatment options enhances participation.
- Support systems: Providing access to counseling and support groups can alleviate emotional distress.
- Lifestyle modifications: Encouraging healthier habits may influence treatment efficacy and overall well-being.
"Research advancement in anaplastic carcinoma is not just about science; it’s about improving lives through innovative care models."
As we look to the future, it is crucial that research continues to focus on these trends and integrative approaches. This will enable a better understanding of anaplastic carcinoma, ultimately leading to improved management and survival rates for patients affected by this formidable disease.
The End
The conclusion serves as the final opportunity to encapsulate the main discussions and insights surrounding anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid within this article. It highlights not only the critical findings but also emphasizes the unique challenges posed by this malignancy in clinical practice. The need for a nuanced understanding of this aggressive cancer cannot be overstated.
Summary of Key Points
In the preceding sections, the article has outlined several significant elements related to anaplastic carcinoma:
- Pathophysiology: Understanding genetic mutations is key. Changes in genes like TP53 and RAS play a vital role.
- Clinical Presentation: Symptoms can be vague, but rapid growth of a thyroid mass is alarming.
- Diagnosis Techniques: Both imaging and histopathology are essential for accurate diagnosis.
- Treatment Options: Surgery combined with radiation therapy is preferred, though chemotherapy and targeted therapies can be considered.
- Prognosis: Generally poor, with survival rates lower than many other cancers, necessitating close consideration of factors influencing outcomes.
- Recent Advancements: New therapeutic agents and biomarkers offer promise for future treatment pathways.
This summary pinpoints the multifaceted nature of anaplastic carcinoma, emphasizing that a multidisciplinary approach is essential for optimal management.
Call for Continued Research
The field of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma requires further investigation to enhance understanding and treatment outcomes. As this type of cancer is rare and aggressive, ongoing research can lead to several beneficial aspects:
- Identifying Molecular Targets: More studies on the genetic landscape of these tumors can unveil new treatment avenues.
- Developing Innovative Therapies: Efficient drug delivery methods and combination therapies need exploration to overcome resistance.
- Improving Early Detection: Biomarkers identified through research could facilitate earlier diagnosis, improving survival chances.
- Evaluating Quality of Life: Future studies should also focus on the psychosocial effects on patients, as improving their quality of life remains crucial.
Overall, it is clear that anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid requires enhanced research efforts. Stakeholders in the medical and academic communities must collaborate to advance knowledge and develop new treatment strategies. Only through such a concerted effort can we hope to improve patient outcomes and explore effective ways to combat this formidable disease.







